Please select root levels for the menu
NZ Plants
Concepts
Ground tissue
The ground tissue system acts as a 'filling' or 'connective' tissue located to the inside of the epidermis and around the vascular tissue. Parenchyma, collenchyma and sclerenchyma tissue are commonly found in ground tissue.
Parenchyma tissue
This is the most common component of the ground tissue system and consists of living cells with thin walls.
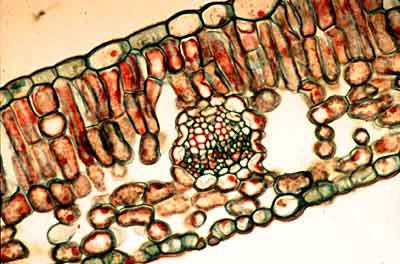

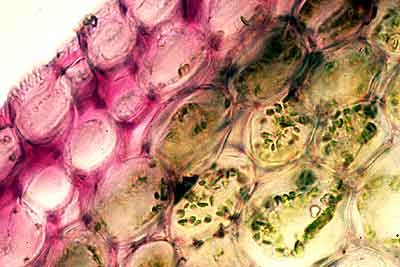
Collenchyma tissue
This is also a living tissue, but one that has an elongated shape and thick accumulations of wall material that are unevenly deposited. Because this wall material has a high pectin content collenchyma cells are able to grow and stretch as the stem elongates. This tissue functions to give support to young, growing stems and leaves.


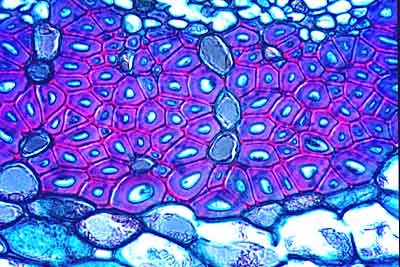
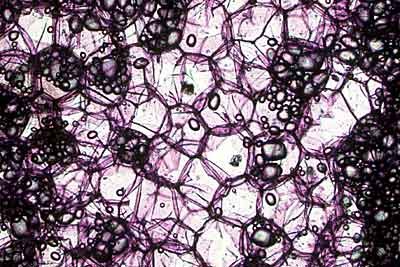
Sclerenchyma tissue
The cells of this tissue are usually dead at maturity, narrow in diameter and very long and overlapping. Before they die, these cells deposit an additional (secondary) wall with a high cellulose content that is uniformly thick. Such cells mature after stem elongation is complete and function to give great strength to older stems.