Please select root levels for the menu
NZ Plants
The vascular tissue system
The vascular tissue system is in the form of bundles or cylinders
Vascular tissue appears as individual bundles in young stems and as a solid cylinder in older, woody stems. It consists of water conducting and sugar conducting cells and may also contain strengthening fibre cells (sclerenchyma) and storage cells(parenchyma).
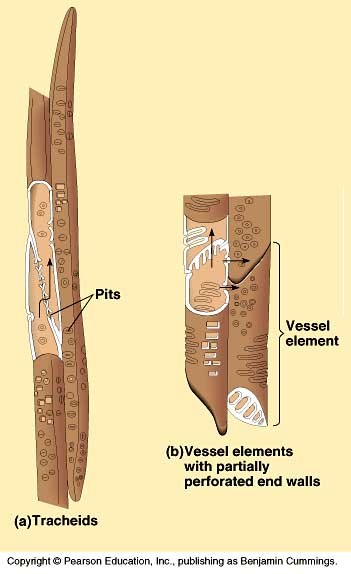
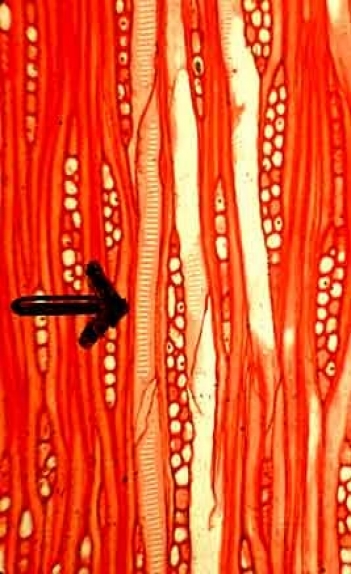
Conducting water: xylem cells
Xylem cells are dead when mature and functional with their empty interior serving as a conduit for the passage of water. They are often subjected to strong negative pressure and their collapse is prevented by the presence of strong secondary cell walls with a high cellulose and lignin content.

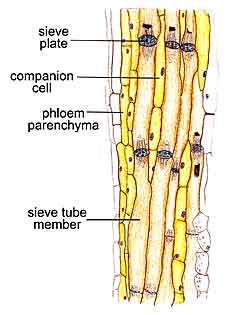
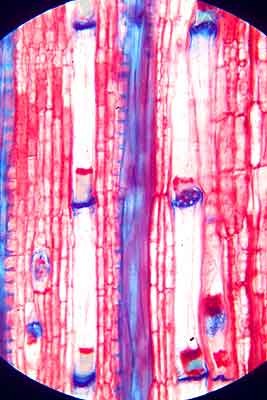
Conducting sugars: phloem cells
Phloem cells are living when functional. They are often subjected to strong positive pressure.